A receding hairline is more than just having less hair. It is a condition that can be brought on by a variety of reasons. Hair loss may have a significant psychological impact on many people, both men and women.
This article will go over what causes a receding hairline, how it’s diagnosed, and whether or not treatments work.
Age and receding hairline
Men’s receding hairlines might occur as they age. Alopecia, or hair loss, can be treated surgically or with drugs in many situations.
Women are more likely than males to have thinning hair or a receding hairline. Women, on the other hand, might have a receding hairline. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and traction alopecia are two instances.
What signs indicate a receding hairline?
A receding hairline in males can occur at any moment after puberty. Many men have a receding hairline by the time they reach their late 30s. The procedure often begins above the temples.
The hairline then goes back over the top of the head. This frequently results in a ring of hair around the top of a bare scalp. On top, thinning hair may continue to grow.
A receding hairline can start above the temples as well, however, hair in the centre may stay closer to the brow. This V-shaped hair growth in the front is commonly referred to as a “widow’s peak.”
Although the sides and back of the head can ultimately go bare, most men are left with some hair unless they shave it entirely off. In women, the sides and back are usually left alone, but the portion expands and thins significantly over the top of the head.
What is the cause of a receding hairline?
About 100,000 hairs sprout from follicles under the skin’s surface on the average person’s scalp. These hairs fall off eventually, only to be replaced by new hairs. Every day, you may lose hundreds of hairs. A receding hairline can occur if hair follicles are damaged or if there is a medical cause that disrupts the growth cycle.
Ancestral history
A receding hairline appears to be an inherited condition, with hair follicles being too sensitive to particular male hormones. Men with a family history of baldness are more prone to have hair loss. The onset of hair loss is frequently consistent from generation to generation.
Changes in hormones
Hormonal changes may also induce female pattern hair loss, however, the involvement of hormones in female pattern hair loss is less understood than in male pattern hair loss. Menopause, for example, can cause hair loss, although the hairline does not necessarily alter.
What causes a receding hairline?
A dermatologist should be consulted to determine the type of hair loss you are having and the reason. Your doctor will want information about your personal and family medical history.
A “pull test” is one type of test that your doctor may perform. They will pluck on a few hairs lightly to see how many fall out and how readily they fall out.
A sample of scalp tissue or hairs may be useful in determining whether a scalp infection is causing hair loss. A biopsy involves your doctor removing a small piece of tissue from the damaged area of your body. A lab will examine the tissue sample for evidence of infection or illness.
You may also get a blood test to rule out illnesses like thyroid disease that might be causing your hair loss.
What is the treatment for a receding hairline?
You won’t require treatment if your receding hairline is merely a function of aging and not the result of an infection or other medical concern. Medication may be required if hair loss is caused by a medical problem.
Medications
An immunological problem may necessitate the use of medications such as prednisone to inhibit an excessive immune response.
Medication such as minoxidil (Rogaine) may be beneficial if you wish to try to reduce or reverse hair loss.
This OTC medication is a liquid that is applied to the scalp. One of the possible negative effects is scalp inflammation. Minoxidil is more successful in restoring hair growth in smaller parts of the scalp than in larger areas.
Finasteride (Propecia) is another medication that may aid in hair growth. Finasteride side effects include decreased sex drive and an increased risk of prostate cancer.
Surgery
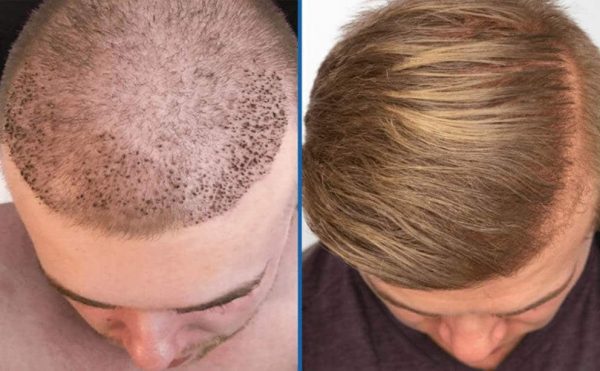
Hair restoration surgery is one surgical option for a receding hairline. It entails transplanting tiny portions of the scalp and hair follicles from the back of the head to regions where hair has stopped growing. These skin plugs may continue to develop hair normally in their new position. Hair may continue to grow normally in the regions where the plugs were placed.
What are the chances of a receding hairline?
A receding hairline might be the initial step toward baldness, or it can be a little shift in your hairline that never worsens. Predicting how far your hairline will recede can be difficult.
Looking at the hair loss pattern of a parent or sibling might sometimes provide a hint. Fortunately, there are drugs and techniques that have been shown to be beneficial in restoring hair growth in afflicted parts of your head. A discussion with your dermatologist is a wonderful place to begin.