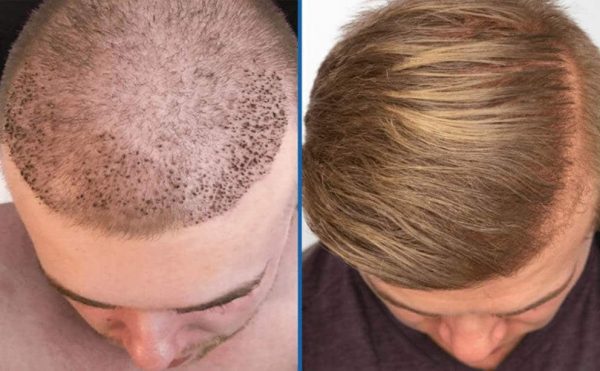
Most of us take our locks for granted, just as we do our health and youth – until they’re gone. For many people, a hair transplant can help restore what seems to be a complete – or at least fuller – head of hair.
If thinning on top or becoming bald disturbs you, the surgery might help you feel more confident about your appearance. But first, consult with your doctor about what to expect before and after the procedure.
What Exactly Is a Hair Transplant?
It is a form of surgery that transfers existing hair to fill in areas with sparse or no hair. Doctors have been doing these transplants in the United States since the 1950s, although procedures have evolved significantly in recent years.
You normally get the procedure at the doctor’s office. First, the surgeon cleans your scalp and injects medication into the back of your skull to numb it. Your doctor will select one of two transplant methods: follicular unit strip surgery (FUSS) or follicular unit extraction (FUE).
The surgeon uses FUSS to remove a 6- to 10-inch piece of skin from the back of your skull. They lay it aside and sew the scalp closed. This place is quickly concealed by the hair that surrounds it.
The surgeon’s team next separates the severed scalp strip into 500 to 2,000 microscopic grafts, each containing one or a few hairs. The amount and kind of grafts you receive are determined by your hair type, quality, color, and the size of the region being transplanted.
The surgeon’s staff will shave the back of your scalp if you get the FUE operation. The doctor will next remove hair follicles one by one. The wound heals with little spots that your natural hair will hide.
After then, the processes are the same. The surgeon cleans and numbs the region where the hair will be placed, then cuts holes or slits using a scalpel or needle and gently implants each transplant in one of the holes. Other team members will most likely assist them in planting the grafts.
The procedure will take between 4 and 8 hours, depending on the amount of the transplant. If you continue to lose hair or decide you desire thicker hair, you may require another operation in the future.
Recovery and Expectations
Your scalp may be quite sensitive after surgery. You may need to take pain relievers for a few days. For at least a day or two, your surgeon will have you wear bandages over your scalp. They may also give you an antibiotic or an anti-inflammatory medication to take for a few days. Most patients are able to return to work within 2 to 5 days of the procedure.
The transplanted hair will fall out after 2 to 3 weeks of surgery, but you should observe new growth within a few months. After 6 to 9 months, most people will notice 60% new hair growth. Some surgeons give minoxidil (Rogaine), a hair-growth treatment, to enhance hair growth following transplantation, although it’s unclear how well it works.
Treatment Risks and Costs
The cost of a hair transplant varies greatly depending on the volume of hair moved, but it typically ranges from $4,000 to $15,000. Most insurance policies don’t cover it.
Transplants, like any other type of surgery, include inherent hazards, including bleeding and infection. Scarring and unnatural-looking new hair growth are also possibilities.
Folliculitis is an inflammation or infection of the hair follicles that occurs around the time new locks begin to form. Antibiotics and compresses can ease the condition. Shock loss occurs when you abruptly lose some of your original hair in the place where you obtained the new strands. However, it is not always permanent.
Discuss these concerns with your doctor, as well as how much improvement you can expect from the operation. They can advise you on if it is a good option for you.
How successful are various hair transplant techniques?
Hair transplants try to restore hair growth to regions of the scalp with minimal or nonexistent growth. They are excellent therapies for a variety of hair loss conditions, but they cannot prevent future hair loss. People may require follow-up transplants for long-term outcomes.
Hair loss and thinning hair are natural parts of aging, but they can also be caused by a medical condition or scalp trauma. Some persons who have hair loss may choose for a hair transplant for aesthetic or reconstructive purposes.
This article examines the success rates of several forms of hair transplants, as well as how long they last and any potential negative effects.
Hair transplant types
During a hair transplant, a surgeon would take follicles from a thick hair location, such as the back of the head, which will be referred to as the donor area. They then insert the follicles into microscopic perforations in the afflicted scalp region.
Hair transplants are classified into two types:
- Follicular unit strip surgery (FUSS): A strip of skin will be removed from the donor region and the incision will be closed with stitches. They will next use a microscope to split the donor skin into small follicular units containing one or more hair follicles, which will be inserted into the appropriate location.
- Follicular unit extraction (FUE): The surgeon will pluck follicles from the donor region with a small punch instrument. Although some scarring will result from this operation, it will be less visible, and the client will likely not require sutures.
Both strategies are successful, but in some circumstances, they provide distinct outcomes. According to the authors of a 2019 research, FUE needs more skill and takes longer than FUSS, but it can give excellent outcomes if the surgeon has extensive experience with the method.
In most cases, the donor area is the side or back of the head. Taking skin from the chin, back, or chest, on the other hand, can be useful. Body hair may be useful for persons who lack thick hair on the back or sides of their heads.
Some investigation
According to a reliable source, extracting body or beard hair takes more time and requires more skill than taking scalp hair. However, according to another research According to Trusted Source, the body and beard can be a “great source” of donor hair for hair transplants.
Each surgery takes several hours, depending on the number of follicles implanted, and both include
Rates of success
Hair transplants are successful treatments for regrowing hair after a variety of reasons of hair loss. The success rate of hair transplant surgery is determined by a variety of factors, including the surgeon’s ability and expertise, as well as the thickness of the donor hair.
Hair transplantation, according to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS), might result in a little increase in hair fullness. Skin flap surgery, tissue expansion, or scalp reduction procedures may be used for drastic modifications.
There are no significant studies that provide exact success rates for hair transplants. Several minor studies and papers, on the other hand, give some information concerning the efficacy of these techniques.
According to one study, the majority of participants who had FUE utilizing body or beard hair coupled with scalp hair were happy with the outcomes after an average of 2.9 years of follow-up. The mean overall satisfaction score among 79 participants was 8.3 out of 10.
Another study’s findings imply that combining platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment with FUE improves the success rate of FUE hair transplants. After 6 months, all participants in the PRP group had more than 75% hair regrowth. They saw faster gains in hair density and skin repair than the non-PRP group.
Here’s more information on PRP for hair loss.
How long do hair transplants last?
In most situations, a successful hair transplant results in thicker-looking hair. They may, however, continue to have hair thinning and loss following the surgery, giving their hair an unnatural or uneven appearance. People may require follow-up transplants for longer-lasting benefits.
According to the ASPS, some of the transplanted hair follicles may fail to “take.” When these follicles die, no new hair develops in its place.
The ASPS also warns consumers that they may require a “touch-up” operation. This technique might assist by filling in any gaps or merging the follicles for a more natural appearance.
Individuals should follow their surgeon’s post-procedure recommendations for the greatest outcomes. This increases their chances of having a successful hair transplant. For several weeks, a person may need to avoid vigorous activities and exercise. They should also wait a few days before shampooing their hair.
Adverse consequences
According to the ASPS, hair transplants are typically safe when performed by a skilled, experienced surgeon. Even with successful hair transplants, certain negative effects may occur.
Bleeding or infection
Hair transplants need incisions or cuts in the skin. A surgeon makes an incision on the scalp to retrieve the donor follicles and microscopic incisions on the scalp to insert the follicles. With any incision, there is a danger of infection or excessive bleeding.
Scars
Scarring is also a possibility in both the donor and transplant areas. Before deciding to get the treatment, a person should discuss the risks with their surgeon.
The FUSS procedure typically results in a lengthy, linear scar where the surgeon removes a strip of skin from the scalp. As new hair comes in around the scar, it may become concealed. It may be apparent, though, if it widens during healing, the surrounding hair is sparse, or the person wears it short in style.
The FUE treatment may potentially cause scars in the area where the follicles were extracted with the punch instrument by the surgeon. These scars, however, may not be as extensive as the FUSS scar.
A person may develop raised pimples around the transplanted hair in some circumstances. These pimples may be hidden when the hair comes back.
Swelling and pain
Some patients may have discomfort while their skin heals following the treatment. To aid with this, their surgeon may prescribe pain medicines. As the skin heals, they may experience swelling in the head and face.
Summary
People with hair thinning and loss may benefit from hair transplant surgery. Although it is not a permanent cure for thinning hair, it can help restore hair fullness and self-confidence in many people.